
#Minitab control chart how to#
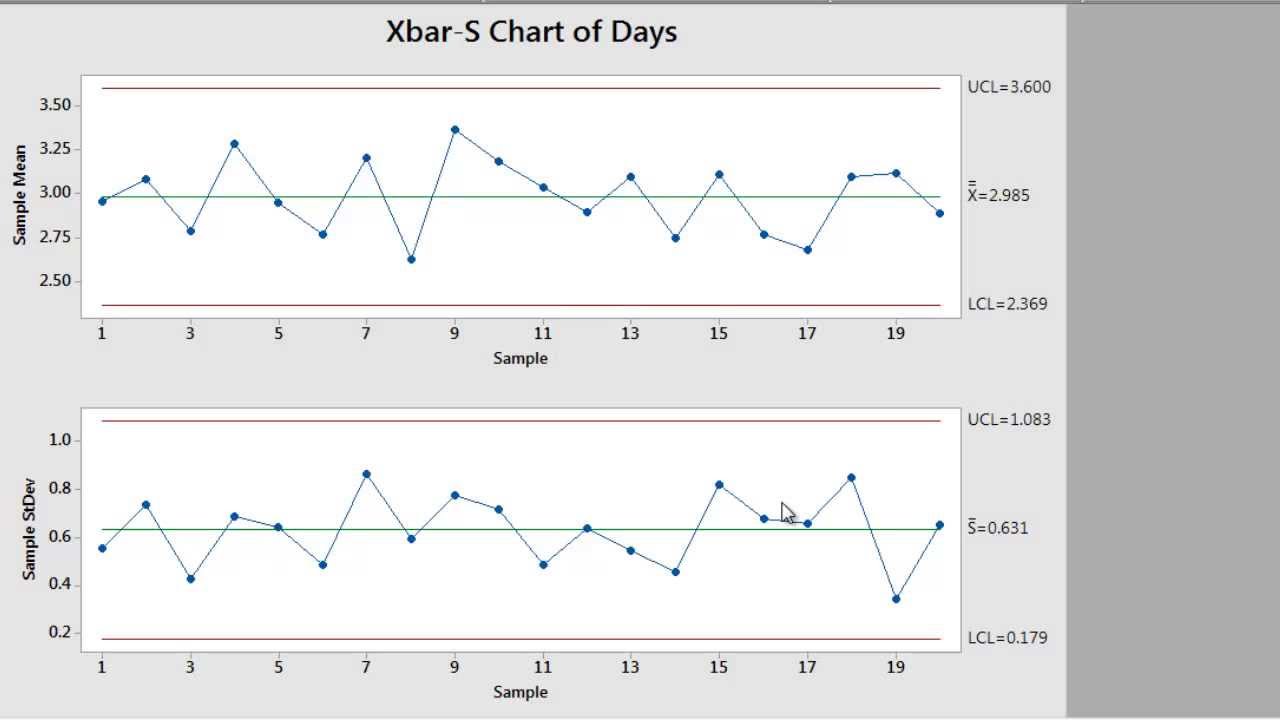
This includes an overview of how to evaluate models and interpret results. Next, the course moves onto model building, where students will learn how to handle regression equations with "wrong" predictors and use stepwise regression to find optimal models in Minitab. Students will also learn how to make predictions for new observations using confidence intervals and prediction intervals. This includes a thorough explanation of statistically significant predictors, multicollinearity, and how to handle regression models that include categorical predictors, including additive and interaction effects. The course then delves into regression analysis in detail, covering the different types of regression models and how to use Minitab to evaluate them. This is followed by an overview of the basics of supervised learning, including how to learn, the different types of regression, and the conditions that must be met to use regression models in machine learning versus classical statistics. The course begins with an introduction to machine learning, where students will gain an understanding of what machine learning is, the different types of machine learning, and the difference between supervised and unsupervised learning. The course also covers tree-based models for binary and multinomial classification. The course covers the fundamental concepts of regression analysis and binary logistic classification, including how to evaluate models and interpret results. This comprehensive course is designed to provide a detailed understanding of the basics of machine learning using Minitab, with a focus on supervised learning. Further investigation is needed to determine the special causes that triggered the unnatural pattern of the process.Course Title: Machine Learning Basics with Minitab We conclude that the process is out of control.

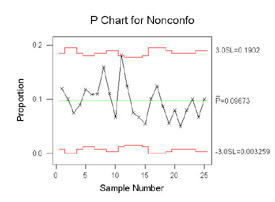
The data point circled above falls beyond the upper control limit. Model summary: Since the sample sizes are not constant over time, the control limits are adjusted to different values accordingly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
